Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a promising technology to a powerful force reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. Across every sector—from government to critical infrastructure, financial services, and global enterprises—AI is transforming both the threats we face and the tools we use to defend against them.
Yet despite the hype, AI is not a silver bullet. It is an amplifier—of capability, of risk, of speed, and of impact.
This article explores how AI is changing cyber risk, defense capabilities, governance, and workforce readiness. It outlines the emerging trends, misconceptions, strategic priorities, and practical steps businesses must take to adopt AI responsibly and securely.

1. Misconceptions and Realities of AI in Cybersecurity
AI Will Not Replace Cybersecurity Professionals
Despite the common fear, AI does not replace security practitioners. Human judgment, context, ethics, and strategic decision-making remain irreplaceable. AI accelerates work; it does not eliminate the need for skilled professionals.
Be brilliant at the basics. AI raises the bar, but fundamentals still win
Shadow AI Is a Growing Risk
Employees are increasingly using generative AI tools without approval or controls. This “Shadow AI” can:
- leak sensitive data
- expose credentials
- violate privacy rules
- bypass logging and monitoring
Unmanaged AI use is quickly becoming one of the highest-impact risks inside organizations.
AI Is Already Embedded Everywhere
From SaaS tools to cloud services, AI capabilities are integrated by default. Opting out is no longer feasible—governance and safe enablement are now mandatory.
2. The Evolving Threat Landscape with AI
Democratization of Cybercrime
- Hyper-personalized phishing
- Deepfake voice/video impersonation
- AI-assisted malware generation
- Scalable social engineering campaigns
Even low-skilled attackers now gain advanced capabilities.
Digital Asset Risk Escalation
With faster routes for theft and laundering, major financial losses can occur in minutes—not hours.
Supply Chain Attacks on AI Models
Threat actors can target:
- model training data
- code dependencies
- cloud pipelines
- forecasting or pricing models
Compromise can silently distort operational or commercial decisions.
Prompt Injection and Model Exploitation
LLM-based products introduce new exfiltration paths, where carefully crafted inputs can trick AI into leaking sensitive information.
3. Defensive Impact and Limitations of AI
Where AI Strengthens Cyber Defense
- SOC triage and enrichment
- noise reduction across alerts
- automated investigation artifacts
- threat pattern detection
- anomaly detection
This significantly reduces MTTR (Mean Time To Repair) and fatigue.
Limitations to Watch
- False positives and false negatives
- Over-automation risks
- Model drift and degradation
- Black-box decisions lacking transparency
- Misplaced trust in AI output
Like DLP programs, AI should follow a staged adoption: monitor → validate → automate.
4. Governance, Trust, and Explainability
Boards, regulators, auditors, and customers expect transparency on how AI is used.
Key Expectations
- Explainability for decisions and recommendations
- Human-in-the-loop for high-impact actions
- Drift detection with retraining pipelines
- Notification obligations when AI models change
- Metrics that measure AI performance and risk
Governance must shift from “technology management” to model risk management.
5. AI Regulation and Framework Guidance
Global regulators—US, EU, UK, Australia, New Zealand—are strengthening expectations around AI responsibility.
Best-Practice Frameworks to Adopt
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework
- EU AI Governance guidance
- OWASP AI Security & LLM Top 10
- ISO/IEC AI Governance standards
Organizations should expand their asset inventories to include all tools, SaaS platforms, and vendors with embedded AI.
6. Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk
AI increases the importance and complexity of vendor governance.
Key Concerns
- Many vendors rely on the same large LLM providers → single points of failure
- Lack of transparency on data provenance
- Weak encryption or storage practices
- No visibility into drift or retraining events
- Inadequate incident response integration
Essential Vendor Due Diligence Areas
- AI governance maturity
- Drift monitoring and reporting
- Data isolation and encryption
- Explainability controls
- SLAs/KPIs for AI performance
- Versioning and change notifications
- Exit strategy and data portability
7. Talent, Workforce, and Organizational Readiness
AI enhances productivity—but it does not close the talent gap.
New Skill Areas Emerging
- AI ethics
- Model governance
- Prompt security
- Post-quantum security
- Red teaming for AI systems
- Agentic AI operations
- Advanced threat modelling
Organizations must invest in continuous upskilling—not one-off training.
Security enables innovation; it gives organizations the confidence to move faster
Cultural Shift
Security teams must move from reactive to proactive, emphasizing:
- Scenario planning
- Tabletop simulations
- Risk-based AI adoption
- Security-by-design thinking
8. Strategy, ROI, and Avoiding the Hype
Organizations should prioritize AI use cases tied to measurable outcomes:
- Reduced cost per investigation
- Lower MTTR (Mean Time to Repair)
- Reduced false positive noise
- Automation of routine tasks
- Tooling consolidation
- Security uplift for business innovation
Adopt AI as a capability—not a product—and align it with business strategy, appetite, and measurable ROI.
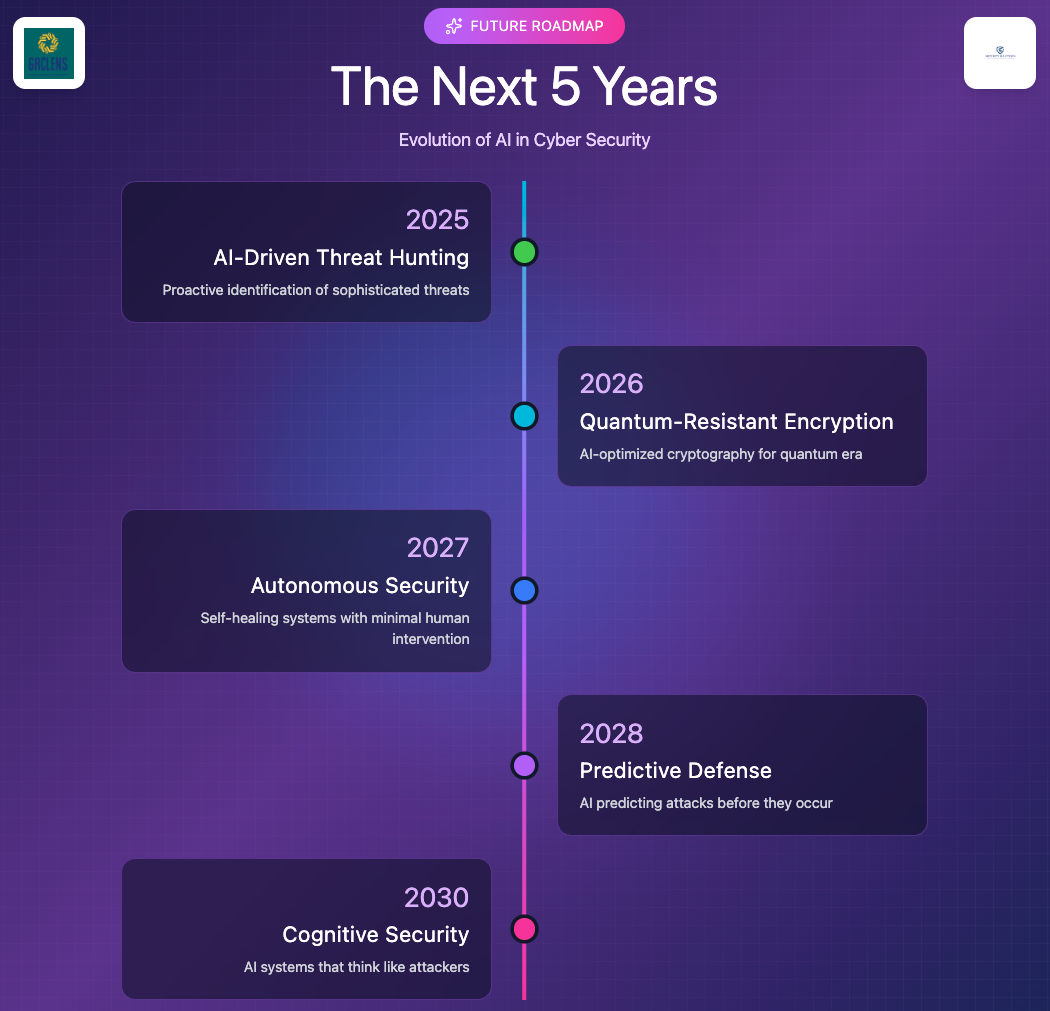
9. The Next 12–24 Months: What to Expect
Threat Trends
- More AI-driven intrusions
- Rapid deepfake impersonation
- Faster value exfiltration
- Increased supply chain manipulation
Defensive Trends
- AI-assisted SOC operations
- Agentic AI for triage and enrichment
- Autonomous but supervised response capabilities
Governance Trends
- Growing regulation
- Mandatory explainability
- AI KPIs reported at board level
Organizational Priorities
- Mature enterprise AI policies
- Formalize AI risk appetite
- Integrate AI into incident response
- Upskill security and technology staff
- Strengthen vendor contracts
Closing Remarks
AI offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance cybersecurity—but it also introduces new risks, new decision points, and new governance responsibilities. Organizations must adopt AI with intention, transparency, and discipline.
Human judgment remains central. AI is a force multiplier, but leadership, governance, and skilled practitioners form the foundation of secure AI adoption.
The organizations that succeed will be those that blend innovation with accountability—embracing AI’s potential while maintaining rigorous oversight, measurable outcomes, and a culture of continuous improvement.
Action Items for Cybersecurity & Business Leaders
For Security Leadership
- Publish an enterprise AI usage policy
- Define risk appetite and governance model
- Require human-in-the-loop for high-privilege actions
- Mandate drift monitoring and transparency for all AI tools
For GRC Teams
- Align AI controls with NIST AI RMF
- Expand risk registers to include AI-specific risks
- Build audit trails for model decisions and outputs
- Embed AI considerations into compliance programs
For SOC & Security Operations
- Pilot AI-assisted triage with staged automation
- Develop metrics for precision, recall, and drift impact
- Conduct periodic red-teaming on AI systems
- Add AI-specific attack scenarios to tabletop exercises
For Third-Party & Supply Chain Risk Teams
- Update due diligence questionnaires for AI
- Require SLAs/KPIs on drift, explainability, and notification
- Add AI governance clauses to contracts and MSAs
- Map vendors using the same LLM providers (concentration risk)
For Asset and Data Management
- Update inventories to identify all AI-enabled systems
- Track data provenance and encryption standards
- Ensure controls for model training, inference, and logs
For CIO/CTO & Product Teams
- Implement secure-by-design AI development
- Establish exit strategies for AI vendors
- Ensure feature toggles for AI-enabled capabilities
For Learning & Development
- Launch structured upskilling programs:
- AI ethics
- Model risk governance
- Prompt security
- Agentic AI
- Post-quantum security
For Board & Executive Teams
You can outsource capabilities, but never accountability
- Request AI explainability dashboards
- Track KPIs, KRIs, and ROI
- Ensure cybersecurity and business strategy remain aligned
How Security Solutions & GRCLens Enable AI-Ready Cyber Resilience
As organisations navigate the accelerating intersection of AI and cybersecurity, the need for strong governance, measurable controls, and real-time visibility has never been greater. This is where Security Solutions—supported by our intelligent GRC platform GRCLens—helps business and cyber leaders build resilience with confidence.
GRCLens, designed with “Intelligent Governance for Digital Trust,” equips organisations with fully integrated workflows across Cyber Risk Management, PCI DSS compliance, Supplier/Vendor Security Assessments, Privacy Impact Assessments, ISO frameworks, and Critical Infrastructure standards (ISO 62443). By consolidating fragmented processes into a single platform, GRCLens provides instant visibility, trend analysis, risk insights, executive reporting, and continuous compliance oversight—with AI-ready governance built in.
Through our consulting services, we help organisations establish AI governance policies, uplift risk management practices, assess third-party AI exposure, strengthen incident response playbooks, develop AI-aligned controls, and implement frameworks such as NIST AI RMF, ISO 42001, ISO 27001/27005, and PSR.
Security Solutions empowers CXOs and Cyber Leaders to align enterprise risk with strategic outcomes, make informed decisions, and adopt AI safely without compromising innovation. Together, our platform + consulting capability deliver a holistic approach to trust, transparency, and operational resilience.


